Topics
-
Number Line
-
Integers
-
Absolute Value
Description
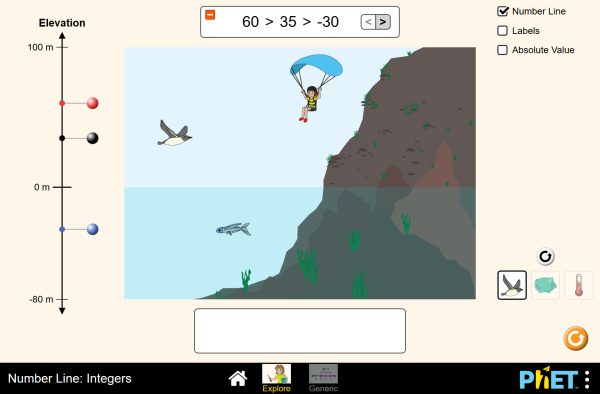
What do elevation, account balances, and temperature have in common? They can all be represented on a number line. Compare integers on a number line and in an inequality statement. Discover the meaning of absolute value.
Sample Learning Goals
- Use positive and negative numbers to represent quantities in multiple contexts.
- Explain the meaning of positive values, negative values, and zero, in multiple contexts.
- Describe the location of a point on a number line with respect to another number.
- Describe the location of a point on a number line with respect to its opposite
- Define the absolute value of a number as its distance from zero.
- Interpret inequality statements as statements about the relative position of two integers on a number line diagram.
Standards Alignment
Common Core - Math
6.NS.C.5
Understand that positive and negative numbers are used together to describe quantities having opposite directions or values (e.g., temperature above/below zero, elevation above/below sea level, credits/debits, positive/negative electric charge); use positive and negative numbers to represent quantities in real-world contexts, explaining the meaning of 0 in each situation.
6.NS.C.6a
Recognize opposite signs of numbers as indicating locations on opposite sides of 0 on the number line; recognize that the opposite of the opposite of a number is the number itself, e.g., -(-3) = 3, and that 0 is its own opposite.
6.NS.C.6c
Find and position integers and other rational numbers on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram; find and position pairs of integers and other rational numbers on a coordinate plane.
6.NS.C.7
Understand ordering and absolute value of rational numbers.
6.NS.C.7a
Interpret statements of inequality as statements about the relative position of two numbers on a number line diagram. For example, interpret -3 > -7 as a statement that -3 is located to the right of -7 on a number line oriented from left to right.
6.NS.C.7b
Write, interpret, and explain statements of order for rational numbers in real-world contexts. For example, write -3 oC > -7 oC to express the fact that -3 oC is warmer than -7 oC.
6.NS.C.7c
Understand the absolute value of a rational number as its distance from 0 on the number line; interpret absolute value as magnitude for a positive or negative quantity in a real-world situation. For example, for an account balance of -30 dollars, write |-30| = 30 to describe the size of the debt in dollars.
6.NS.C.7d
Distinguish comparisons of absolute value from statements about order. For example, recognize that an account balance less than -30 dollars represents a debt greater than 30 dollars.
7.NS.A.1a
Describe situations in which opposite quantities combine to make 0. For example, a hydrogen atom has 0 charge because its two constituents are oppositely charged.
7.NS.A.1b
Understand p + q as the number located a distance |q| from p, in the positive or negative direction depending on whether q is positive or negative. Show that a number and its opposite have a sum of 0 (are additive inverses). Interpret sums of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts.
Version 1.0.1
HTML5 sims can run on iPads and Chromebooks, as well as PC, Mac, and Linux systems.
iPad:
iOS 12+ Safari
iPad compatible sims
Android:
Not officially supported. If you are using the HTML5 sims on Android, we recommend using the latest version of Google Chrome.
Chromebook:
Latest version of Google Chrome
The HTML5 and Flash PhET sims are supported on all Chromebooks.
Chromebook compatible sims
Windows Systems:
Microsoft Edge, latest version of Firefox, latest version of Google Chrome.
Macintosh Systems:
macOS 10.9.5+, Safari 9+, latest version of Chrome.
Linux Systems:
Not officially supported. Please contact phethelp@colorado.edu with troubleshooting issues.