Topics
- Oscillator
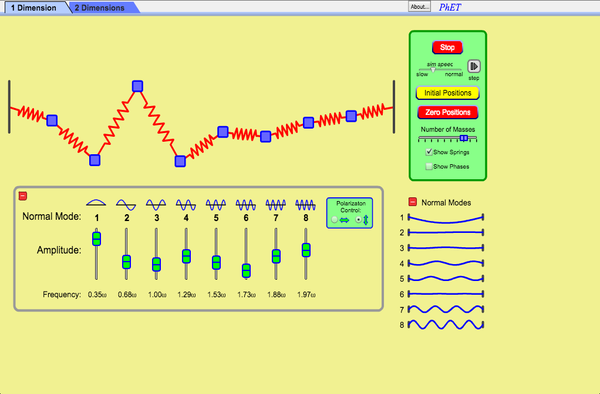
- Normal Modes
- Polarization
- Mass Spring System
- Frequency
- Amplitude
- Phase
Description
Play with a 1D or 2D system of coupled mass-spring oscillators. Vary the number of masses, set the initial conditions, and watch the system evolve. See the spectrum of normal modes for arbitrary motion. See longitudinal or transverse modes in the 1D system.
Sample Learning Goals
- Explain what a normal mode is.
- Explain what are the frequency, the amplitude, and the phase of a normal mode.
- Explain why different normal modes have different frequencies and why higher-numbered modes have higher frequencies.
- Identify how many normal modes a given system has and be able to sketch the individual modes qualitatively, for both 1D and 2D systems.
- Explain the distinction between transverse and longitudinal normal modes in a 1D system.
- Explain how adjusting the phase of a normal mode affects the motion of the system.
- Explain qualitatively how any arbitrary state of the system can be written as a sum of normal modes; that is, explain the superposition principle.
- Explain which properties of the system are set by the initial conditions, which properties are time-independent, and which properties are time-dependent.
- Explain why striking a metal plate in one spot raises the temperature of the plate.