Topics
-
Area
-
Perimeter
-
Fractional areas
-
Scale factors
Description
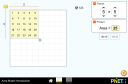
Create your own shapes using colorful blocks and explore the relationship between perimeter and area. Compare the area and perimeter of two shapes side-by-side. Challenge yourself in the game screen to build shapes or find the area of funky figures. Try to collect lots of stars!
Sample Learning Goals
- Find the area of a shape by counting unit squares
- Describe the relationship between area and perimeter
- Build shapes with a given area and/or perimeter
- Find the area of an irregular shape by decomposing into smaller, regular shapes (e.g., rectangles, triangles, squares)
- Determine the scale factor of similar shapes
- Generalize how area and perimeter change when scaling shapes
Standards Alignment
Common Core - Math
3.MD.C.5
Recognize area as an attribute of plane figures and understand concepts of area measurement.
3.MD.C.5a
A square with side length 1 unit, called "a unit square," is said to have "one square unit" of area, and can be used to measure area.
3.MD.C.5b
A plane figure which can be covered without gaps or overlaps by n unit squares is said to have an area of n square units.
3.MD.C.6
Measure areas by counting unit squares (square cm, square m, square in, square ft, and improvised units).
3.MD.C.7
Relate area to the operations of multiplication and addition.
3.MD.C.7a
Find the area of a rectangle with whole-number side lengths by tiling it, and show that the area is the same as would be found by multiplying the side lengths.
3.MD.C.7b
Multiply side lengths to find areas of rectangles with whole-number side lengths in the context of solving real world and mathematical problems, and represent whole-number products as rectangular areas in mathematical reasoning.
3.MD.C.7c
Use tiling to show in a concrete case that the area of a rectangle with whole-number side lengths a and b + c is the sum of a × b and a × c. Use area models to represent the distributive property in mathematical reasoning.
3.MD.C.7d
Recognize area as additive. Find areas of rectilinear figures by decomposing them into non-overlapping rectangles and adding the areas of the non-overlapping parts, applying this technique to solve real world problems.
3.MD.D.8
Solve real world and mathematical problems involving perimeters of polygons, including finding the perimeter given the side lengths, finding an unknown side length, and exhibiting rectangles with the same perimeter and different areas or with the same area and different perimeters.
6.G.A.1
Find the area of right triangles, other triangles, special quadrilaterals, and polygons by composing into rectangles or decomposing into triangles and other shapes; apply these techniques in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems.
Version 1.1.20
HTML5 sims can run on iPads and Chromebooks, as well as PC, Mac, and Linux systems.
iPad:
iOS 12+ Safari
iPad compatible sims
Android:
Not officially supported. If you are using the HTML5 sims on Android, we recommend using the latest version of Google Chrome.
Chromebook:
Latest version of Google Chrome
The HTML5 and Flash PhET sims are supported on all Chromebooks.
Chromebook compatible sims
Windows Systems:
Microsoft Edge, latest version of Firefox, latest version of Google Chrome.
Macintosh Systems:
macOS 10.9.5+, Safari 9+, latest version of Chrome.
Linux Systems:
Not officially supported. Please contact phethelp@colorado.edu with troubleshooting issues.